ADHD is a mental health problem that causes excessive impulsivity and hyperactivity. Patients with ADHD may also have difficulty concentrating on a single task or remaining stationary for long periods.
Many people experience inattention and energy fluctuations. This occurs more frequently and to a greater extent in people with ADHD than those without the disorder. It has the potential to have a significant impact on their schooling, employment, and personal lives.
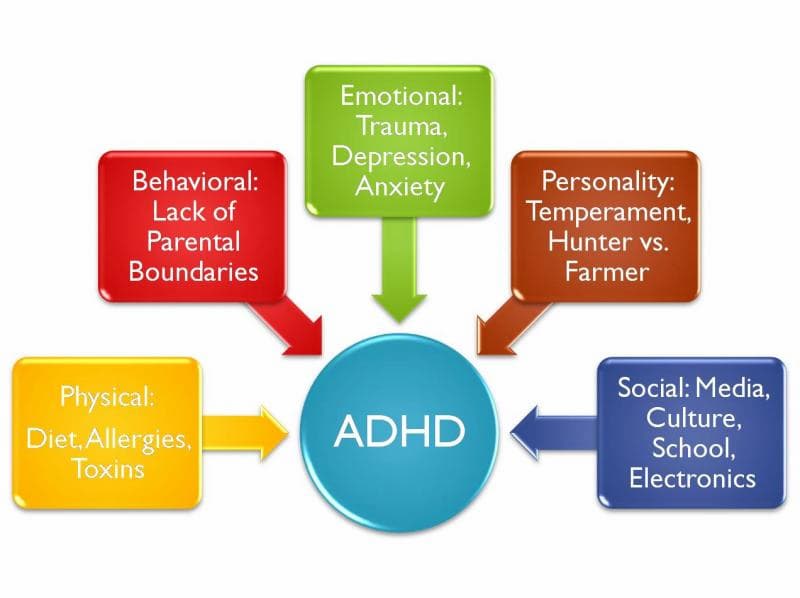
What Causes ADHD?
Even though ADHD is quite common, doctors and researchers are still not sure what causes this condition. It’s thought to have neurological origins. Genetics could also be a factor.
According to research, dopamine deficiency is a component of ADHD. Dopamine is a chemical in the brain that helps transmit signals from one nerve to another. It helps in the elaboration of emotional responses and movements.
Other studies suggest that the brain has a structural difference. According to the findings, those with ADHD had a lower grey matter volume. Gray matter refers to the parts of the brain that help with:
· Speech.
· Self-control.
· Making a decision.
· Control of the muscles.
Potential causes of ADHD, including smoking during pregnancy, are still being studied by researchers.
ADHD Symptoms
ADHD has been linked to a variety of behaviors. The following are a few common ADHD symptoms:
· Struggling to focus on tasks.
· Forgetting when it comes to finishing assignments.
· Being sensitive to distraction.
· Struggling to stay still.
· Interrupting a conversation in the middle.
Different aspects of ADHD can have other signs and symptoms, such as hyperactivity, difficulty focusing, or impulsivity. A person who is susceptible to impulsivity and hyperactivity may:
· Find it challenging to sit still or remain seated for a long time, such as in class, or play or carry out activities quietly.
· Excessive talking.
· Find it tough to wait for their turn.
Someone who is having difficulty focusing may:
· Make frequent errors or miss details when studying or working.
· Find it difficult to stay focused while listening, reading, or conversing.
· Having a hard time keeping track of their daily tasks.
· Items are frequently lost.
· Be easily distracted by minor events in their environment.
You or your child may experience some or all of these symptoms if you have ADHD. Depending on the type of ADHD you have, your symptoms will vary.
Types of ADHD
The American Psychological Association (APA) has classified ADHD into three types to make diagnosis more consistent. These types are predominantly hyperactive-impulsive or predominantly inattentive, or a combination of both.
Predominantly Inattentive
This type of ADHD makes it difficult for people to focus, complete tasks, and follow instructions.
According to professionals, many kids with inattentive ADHD may go undiagnosed because they do not disrupt the classroom. According to research, this is more likely among girls with ADHD.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive
Hyperactive and impulsive behavior are characteristics of this type of ADHD. This includes fidgeting, interrupting people while they’re speaking, and not being able to wait their turn.
Although inattention is less of an issue with this type of ADHD, people with hyperactive-impulsive ADHD may still find it difficult to focus on tasks.
Combined Hyperactive-Impulsive and Inattentive
This is the most common form of (ADHD). In this type of ADHD, people experience both inattentive and hyperactive symptoms. These include an inability to focus, a tendency towards impulsivity, and relatively high activity and energy levels.
How you or your child is treated depends on the type of ADHD you or your child has. Your class may change over time, and as a result, your therapy may change too.
ADHD Diagnosis and Testing
There is no single test that can determine whether you or your child has ADHD. A study highlighted the advantages of a new test for diagnosing adult ADHD. However, many clinicians consider that an ADHD diagnosis cannot be determined based on a single test.
A doctor will evaluate any symptoms you or your child has had in the previous six months to determine a diagnosis.
Your doctor will ask teachers or family members and go over your symptoms using checklists and rating systems. They will also do a physical examination to check out any other health issues.
If you or your child feels they might have ADHD, see a doctor about getting an evaluation. You can also speak with your child’s school counselor. Schools evaluate students regularly for issues that may be harming their academic achievement.
Provide notes and observations about your or your child’s behavior to your doctor or counselor for the assessment.
They may recommend you or your child to an ADHD specialist if they suspect ADHD. They might also recommend seeing a psychiatrist or neurologist, depending on the diagnosis.
ADHD Treatment
Behavioral therapy, medication, or a combination of the two are commonly used to treat ADHD.
One type of therapy is psychotherapy, sometimes known as talk therapy. In talk therapy, you or your child will discuss how ADHD affects your life and how to manage it.
Behavioral therapy is another sort of therapy. This therapy can help you or your child learn to be more in control and aware of their actions.
When you have ADHD, medication can be beneficial. ADHD drugs work by altering brain chemicals, which enables you to control your impulses and actions better.
ADHD Medication
The two main types of medicines used to treat ADHD are stimulants and non-stimulants.
Central nervous system (CNS) stimulants are the most often used ADHD medications. These drugs work by increasing dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain. These drugs include amphetamine-based stimulants (Adderall) and methylphenidate (Ritalin).
If stimulants are not working or are causing you or your child problems, your doctor may recommend a non-stimulant drug. Certain non-stimulant medications work by increasing the brain’s norepinephrine levels. Some antidepressants, such as bupropion (Wellbutrin) and atomoxetine (Strattera), are among these drugs.
ADHD medications can have several benefits as well as drawbacks.
Natural Remedies for ADHD
Several treatments have been proposed to help improve the symptoms of ADHD.
Making lifestyle adjustments, for starters, may help you or your child manage ADHD symptoms. The following are recommendations from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), such as consuming a nutritious and well-balanced diet, completing at least 60 minutes of daily physical activity, getting enough sleep, reducing daily screen time (phones, laptops, and television).
Is ADHD a Disability?
Although ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder, it is not considered a learning disability. However, it is possible that some people with ADHD also have learning disabilities.
Teachers can map out unique recommendations for a student with ADHD to help relieve any impact on learning for children. Allowing extra time for assignments and tests and creating a personal reward system are examples of this.
ADHD can have long-term consequences, even if it isn’t officially a disability.
Coexisting Conditions
Other mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are common among people with ADHD.
Depression
If you or your child has ADHD, you’re more likely to suffer from depression. According to a study, nearly 50% of adolescents with ADHD had significant depression or anxiety, compared to only 35% of those without the disorder. According to studies, up to 53.3 percent of adults with ADHD may also suffer from depression.
This may seem like an unfair double whammy, but both conditions have treatments available. In reality, many of the therapies are similar. Both disorders can be treated with talk therapy. Antidepressants like bupropion can also help with ADHD symptoms.
Conduct and Behavior Disorders
Children with ADHD have more behavior and conduct issues than children without the disorder. Several diseases might develop when a person does not feel understood by those around them.
If they don’t feel understood, they may argue a lot, lose their anger, or intentionally annoy others. These symptoms could indicate an oppositional defiant disorder.
Some people cannot stop themselves from breaking the rules or acting violently against others, such as fighting, bullying, or stealing things that don’t belong to them. This is known as conduct disorder.
Learning Disorder
Some children with ADHD have a learning issue, making it even more challenging to complete their schoolwork. Examples include Dyslexia, which makes reading difficult, or difficulty with numbers or writing.
These difficulties can make it difficult for a child to manage at school and worsen anxiety and sadness. It is important to get care as soon as possible to reduce the intensity of these difficulties.




